XDE Workbench
Our Advanced Physics module is based on XDE Physics, the interactive multi-physics simulation engine designed by CEA List (Laboratory for Integration of Systems and Technology).
Named XDE Workbench, this command dedicates to the creation of the XDE physics simulations. It is the place to:
- Create kinematics constraints
- Specify flexibles behaviour
- Configure physical properties on parts (mass, collisions, friction, ...)
Setup command
XDE Workbench command comes with the Extension "Advanced Physics (beta)". Therefore, you need to add this extension to your experience to benefit from it.
Then, as it requires Xde Physics module to run, you must activate it through the experience settings, and ensure you have access to an XDE license.
Finally, if it is the firts time you add the extension, you must add the command "Xde Workbench" to your decktop menu.
Overview
Use Cases possibilities with XDE
Complex collision
- Complex shape collision
- Force monitoring
- Haptic feedbacks
- Path finding
Cable simulation (1D Elastic)
- Mechanical parameter
- Flexible (Lifting sling)
- Effort distribution
- Stranded cable
Kinematic joint
- DOF with limits
- Force & damping
- Hard & soft joints
Controls
- User grab & moves
- Sequence / Process
User Interface
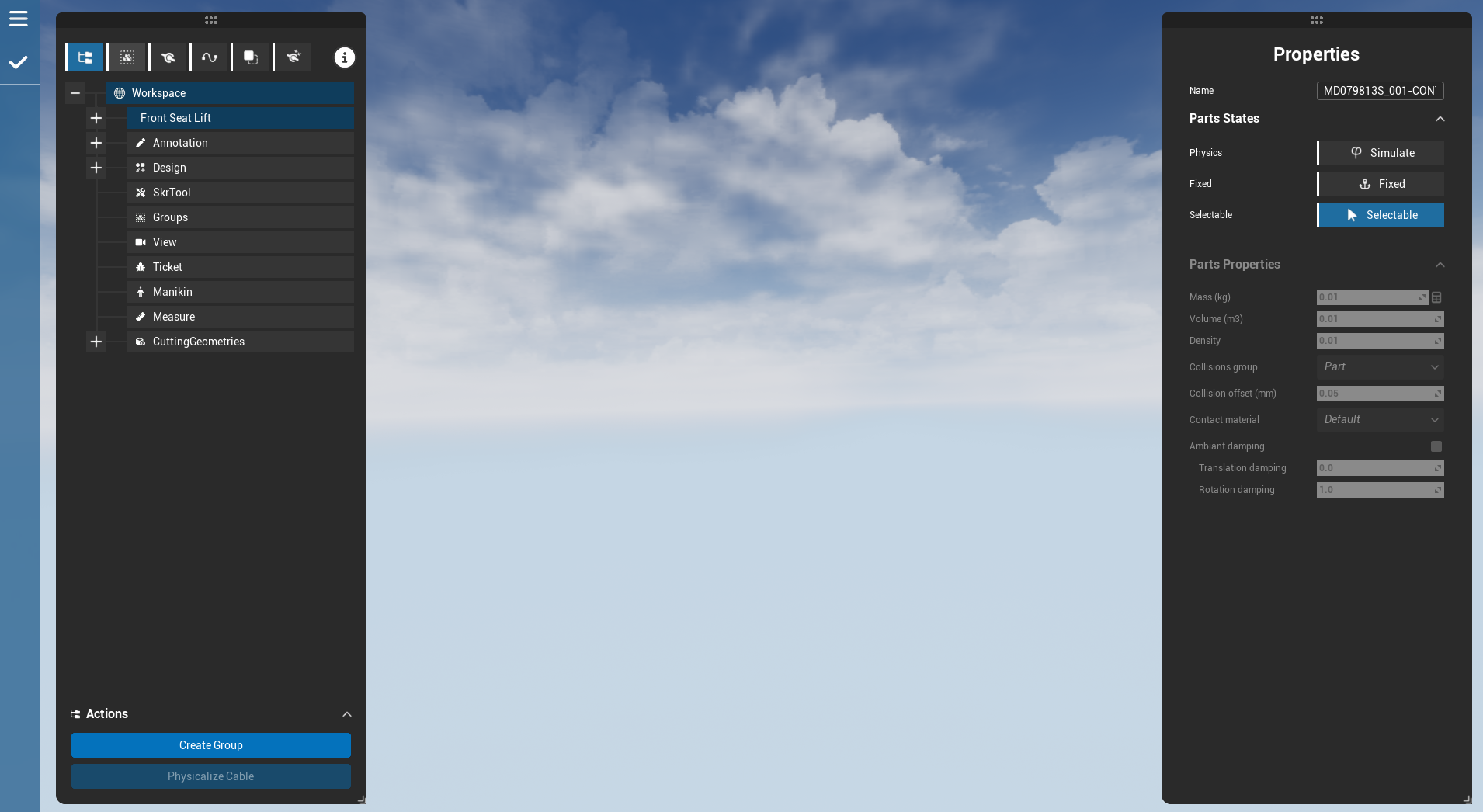
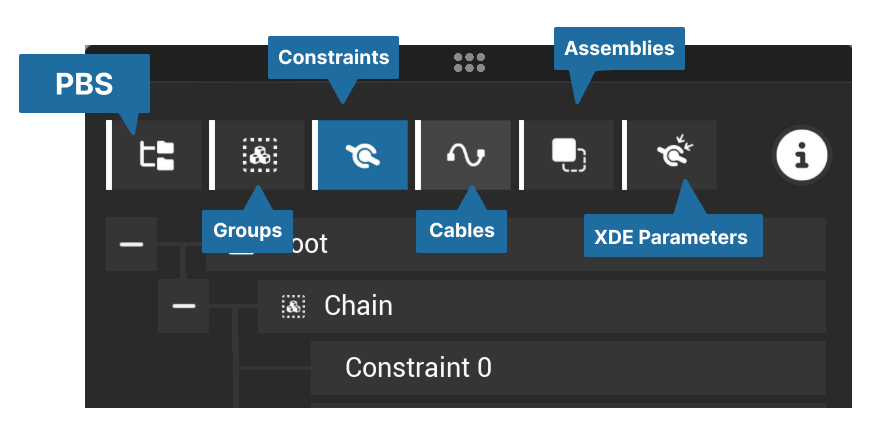
The user interface of the command is composed of two panels. The left panel, dedicated to listing the objects (Hierarchy, groups, constraints, cables, assemblies, ...). The right panel is dedicated to displaying the properties.
Groups
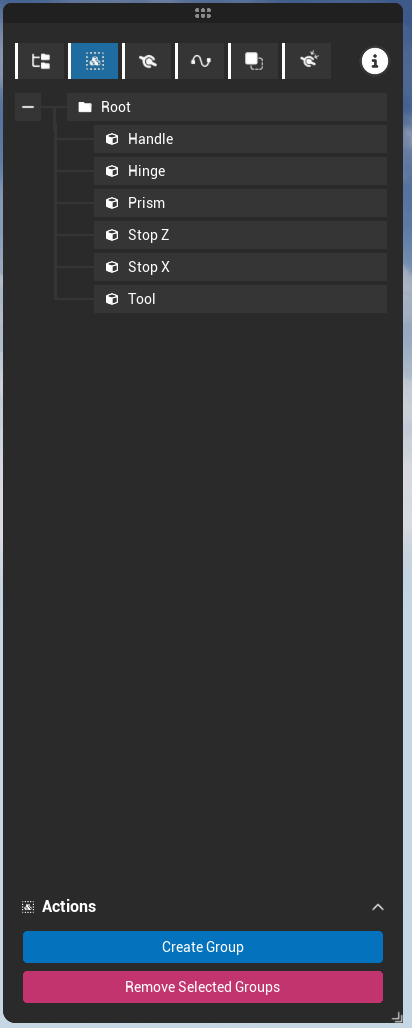
Groups can be created from the Hierachy panel or from the Group panel.
In both cases, the group is created from the current selection. The hierarchy can help selecting multiple parts.
The group panel shows all the created groups.
A group behaves exactly as a part. So they share the same properties. A click on a group displays its properties in the right panel.
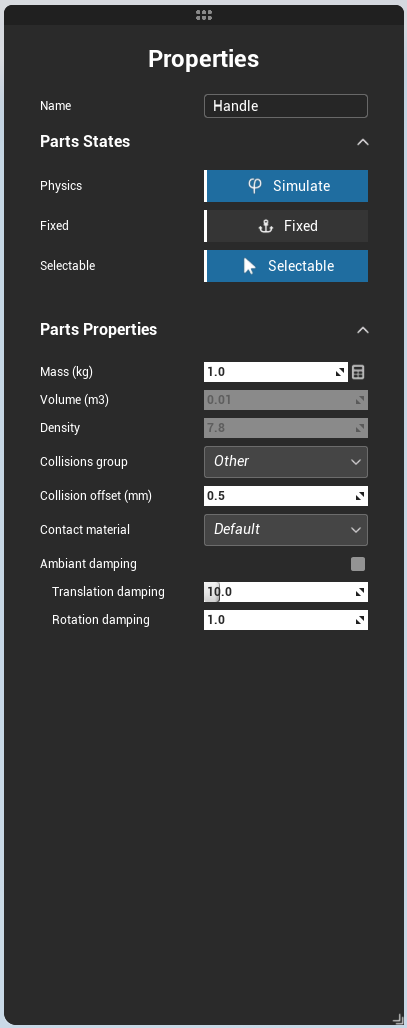
Part properties
Those properties are also applicable to groups that can be considered as parts (for physics). A part have states:
- Simulated: If not simulated, the part is not in the physics engine. Therefore, it can't move, collide, be attached to constraint or cable.
- Fixed: the part is fixed to the world, except if the user manipulates it with a Grab method.
- Selectable: Not directly linked to physics, it is a way to forbid the user manipulating the part.
A part bears the following physical properties:
- Mass (kg): can be computed from the default density and the volume (if computed)
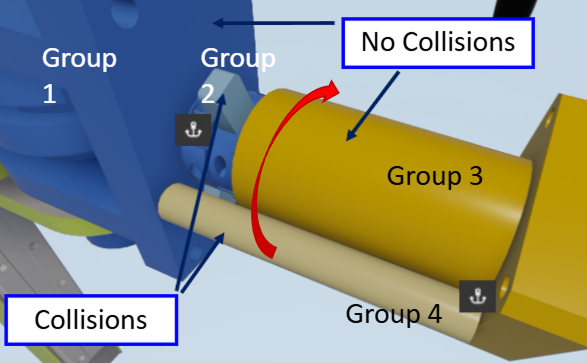
- Collision group: "Part" by default, used to remove collision from certain parts, or split the collisions in multiple groups for optimization purpose.
- Contact material: defines the material type. Contact laws describe then the interaction between different materials. (friction, reaction)
- Ambiant damping: fluid friction between the part and the ambiant fluid (air, water, whatever)
Constraints
Constraints can be created from the constraint tab. Once created, you can edit its properties in the right panel.
Constraints are automatically grouped under "chain" items if the parts they link make a kinematic chain.
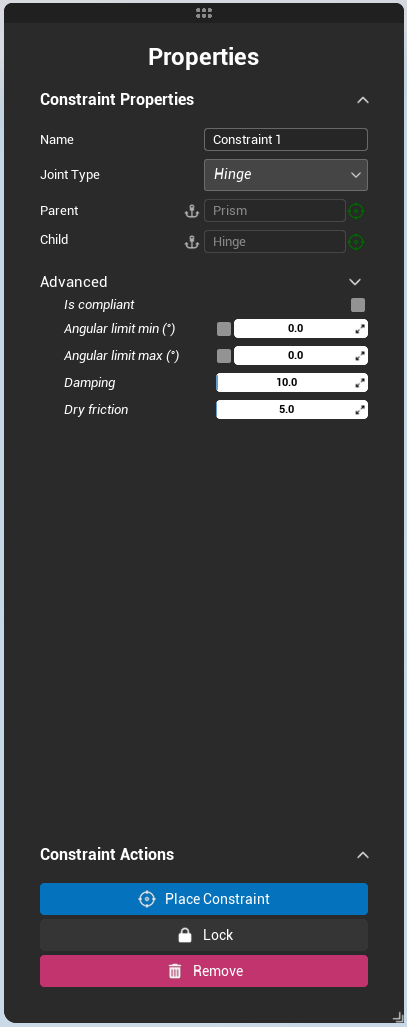
Creation process
- Create New Constraint from the left panel
- Choose the Type
- Set Parent/Child clicking on the target icon
- Fix one on them if necessary clicking on the anchor icon
- Edit Advanced properties if needed (can also be done later on)
- Place constraint clicking on the blue button
Attachement
A constraint must reduce degrees of freedom between two parts.
This attachement is done through the "Parent" and "Child" properties.
Rule to choose parent vs child:
- in general: a part can be child only once
- exception: can be done using the compliant property on a constraint. If a part is child of N constraints, you need N-1 constraints with compliant property enabled.
Joint Types
| Joint Type | Description | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Hinge | Only one rotation allowed | - Is Compliant - Angular limit min in degree - Angular limit max in degree - Damping - Dry friction |
| Prismatic | Only one translation allowed | - Is Compliant - Angular limit min in degree - Angular limit max in degree - Damping - Dry friction |
| Cylindrical | One rotation and one translation (same axis) allowed | - Is Compliant - Limit min in mm - Limit max in mm - Angular limit min in degree - Angular limit max in degree - Damping - Dry friction |
| Helical | One rotation and one translation coupled (one degree of freedom in the end) allowed | - Lead (mm): displacement for 360 deg rotation - Limit min in mm - Limit max in mm - Damping - Dry friction |
| Planar | Two translations allowed. The constraint placement is an axis that describes the normal to the plane | No Properties |
| Ball | Three rotations allowed. The constraint placement is a point | - Is Compliant - Damping |
| Cardan | Two translations allowed. The constraint placement is an axis that describes the normal to the plane | No Properties |
| Point on line | One translation and Three rotations allowed. The constraint placement is an axis that describes the translation axis | No Properties |
Cables
Simulate flexible cables with realistic physical behavior. Cables can be created from Skyreal's cables feature. They support real-time physics for bending, collisions, and deformation, making it easy to design and test cable routing.
Radius:
Cable radius
Total Length:
Current length of the cable, can be updated live
Nodes per meter:
Controls simulation resolution.
Attach Points:
define start, end, and intermediate cable fixations.
Material:
Custom physical properties
- Density: impacts cable mass
- Young modulus: impacts flexibility and stiffness
- Collision Group: enables interaction with other physicalized objects.
Golden Rules
Groups
1- A group corresponds to a rigid assembly of parts.
2- Groups are not mandatory, XDE objects can interact directly with parts
3- You can split a rigid assembly into multiple groups to split the Collision Group parameters.
Kinematics
1- A part can be the child of multiple constraints, but one of those constraints must be set as compliant
2- A compliant constraint can't verify limits and damping
3- Collisions are disabled between two parts linked by a constraint
4- When a part or group is linked to a constraint, it is automatically simulated and takes the default properties.
Advices
-
A correct setup of Parent and Child is necessary for the simulation to compute. For a good readability, you should start from a fix part (root of the mechanism) and go down.
-
Check if there is at least one compliant per closed loop
